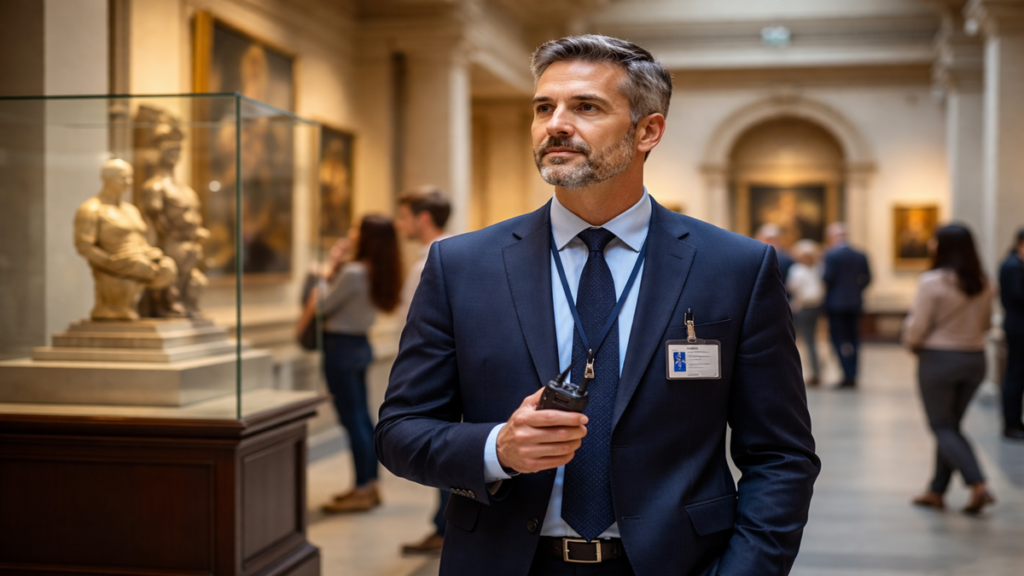
I approach the concept of museumsaufsicht with a sense of respect for roles that often remain invisible to visitors yet are essential to cultural institutions. When people think about museums, they usually focus on exhibitions, architecture, or famous artworks. During my exploration of museumsaufsicht, I realized how central this function is to the everyday life of a museum. It is not simply about supervision or rule enforcement. It represents a structured responsibility that protects collections, supports visitors, and maintains the integrity of shared cultural spaces.
In this article, I explain museumsaufsicht as a professional role and operational system within museums. I focus on responsibilities, workflows, ethical dimensions, visitor interaction, and how this role has evolved in modern institutions. Everything is written in original language, using practical reasoning rather than external references. The goal is to give readers a deep and realistic understanding of what museumsaufsicht truly means.
Understanding the Meaning of Museumsaufsicht
Linguistic and Functional Interpretation
Museumsaufsicht is a German term that can be understood as museum supervision or gallery oversight. Linguistically, it combines the idea of a museum with oversight, responsibility, and attentive presence. Functionally, museumsaufsicht refers to the staff members or structured role responsible for monitoring exhibition spaces, ensuring visitor safety, and protecting cultural assets.
This role exists in nearly every museum worldwide, even if it is called by different names in different languages. What makes museumsaufsicht distinct is its formal recognition as a professional duty rather than an informal task.
Why Museumsaufsicht Is Essential
Museums are public spaces that house irreplaceable objects. Without structured supervision, even the most well designed museum would face constant risks. Museumsaufsicht ensures that artworks are respected, visitors feel secure, and institutional rules are followed consistently.
It acts as a bridge between the institution and the public. The presence of museumsaufsicht communicates care, order, and accountability.
Core Responsibilities of Museumsaufsicht
Protection of Artifacts and Exhibits
One of the primary responsibilities of museumsaufsicht is safeguarding exhibits. This includes preventing physical contact with fragile objects, monitoring environmental risks, and responding quickly to potential threats.
Museumsaufsicht staff are trained to observe subtle behaviors that may indicate risk, such as overcrowding, accidental contact, or deliberate misconduct. Their role is preventive rather than reactive.
Visitor Safety and Guidance
Museumsaufsicht is equally responsible for visitor well being. This includes managing crowd flow, assisting in emergencies, and ensuring accessibility pathways remain clear.
Visitors often turn to museumsaufsicht staff for directions, explanations of rules, or help during unexpected situations. This makes the role both protective and service oriented.
Rule Enforcement With Professional Judgment
Museums have rules regarding photography, touching exhibits, food, and movement. Museumsaufsicht enforces these rules with discretion and professionalism. The goal is not punishment but preservation and respectful behavior.
This requires strong interpersonal skills and situational awareness. Every interaction reflects the museum’s values.
Daily Workflow of Museumsaufsicht
Monitoring Exhibition Spaces
A typical day involves continuous monitoring of assigned galleries. This includes visual scanning, listening for disturbances, and maintaining awareness of visitor behavior.
Museumsaufsicht staff often rotate positions to maintain alertness and cover different sections of the museum.
Communication With Museum Teams
Museumsaufsicht does not operate in isolation. Staff communicate regularly with curators, security teams, visitor services, and management. This coordination ensures that issues are addressed efficiently.
Clear communication channels are critical, especially during special exhibitions or high traffic periods.
Incident Reporting and Documentation
When incidents occur, museumsaufsicht documents them carefully. Reports may include visitor injuries, object damage, or rule violations. These records help museums improve policies and prevent future issues.
Documentation is part of institutional accountability.
Skills and Qualities Required for Museumsaufsicht
Observation and Attention to Detail
A strong museumsaufsicht’s professional notices small changes in behavior or environment. This includes recognizing signs of fatigue in visitors, noticing changes in object placement, or detecting potential hazards.
Attention to detail protects both people and collections.
Communication and Empathy
Museumsaufsicht staff interact with visitors from diverse backgrounds. Clear communication, patience, and empathy are essential. Many situations require calm explanation rather than authority.
Positive interactions enhance the visitor experience.
Ethical Awareness and Responsibility
Museumsaufsicht’s staff hold responsibility over cultural heritage. Ethical awareness guides their decisions, especially when balancing accessibility with preservation.
They must respect both institutional rules and human dignity.
Comparison Between Museumsaufsicht and General Security Roles
| Aspect | Museumsaufsicht | General Security |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Cultural preservation and visitors | Physical security |
| Visitor Interaction | High and service oriented | Limited and authority based |
| Training Emphasis | Art protection and ethics | Threat prevention |
| Environment | Educational and public | Often restricted |
| Decision Style | Discretion and guidance | Enforcement focused |
This comparison highlights why museumsaufsicht’s is a specialized role rather than generic security work.
Museumsaufsicht and Visitor Experience
Creating a Welcoming Environment
Although museumsaufsicht’s involves supervision, its presence should feel supportive rather than intimidating. Professional demeanor and approachable behavior encourage visitors to engage comfortably with exhibitions.
A well trained museumsaufsicht’s enhances the atmosphere of trust.
Supporting Educational Goals
Museums are educational institutions. Museumsaufsicht’s contributes by reinforcing learning environments. By guiding behavior gently, they help maintain quiet, focus, and respect within galleries.
They also answer basic questions that support visitor understanding.
Ethical Dimensions of Museumsaufsicht
Respect for Cultural Sensitivity
Museums often display culturally significant or sensitive materials. Museumsaufsicht’s must be aware of cultural norms and visitor reactions. This sensitivity helps prevent misunderstandings and conflict.
Ethical awareness strengthens institutional credibility.
Balancing Access and Preservation
One of the most challenging aspects of museumsaufsicht is balancing public access with artifact protection. Too much restriction limits learning, while too little risks damage.
Professional judgment is essential in finding this balance.
Training and Professional Development
Initial Training Programs
Museumsaufsicht’s staff typically receive training in museum policies, emergency procedures, visitor interaction, and basic conservation awareness. This foundation prepares them for daily responsibilities.
Training emphasizes prevention rather than reaction.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Museums evolve constantly. New exhibitions, technologies, and visitor behaviors require ongoing training. Museumsaufsicht’s staff must adapt to these changes to remain effective.
Professional development supports long term institutional success.
Museumsaufsicht in Modern Museums
Integration With Technology
Modern museums use surveillance systems, environmental sensors, and digital visitor management tools. Museumsaufsicht’s works alongside these technologies rather than being replaced by them.
Human judgment remains essential even in advanced environments.
Responding to Increased Visitor Diversity
Global tourism and digital exposure bring diverse audiences into museums. Museumsaufsicht’s must navigate language barriers, cultural differences, and varied expectations.
This diversity makes the role more complex and more important.
Challenges Faced by Museumsaufsicht
Physical and Mental Demands
Long periods of standing, constant alertness, and emotional labor can be demanding. Museumsaufsicht’s staff must maintain professionalism even under stress.
Institutions must recognize and support these challenges.
Underestimation of the Role
Museumsaufsicht’s is sometimes undervalued because it operates quietly. This underestimation can affect morale and resources.
Recognizing its importance strengthens museum operations.
The Future of Museumsaufsicht
Expanding Professional Recognition
As museums acknowledge the complexity of visitor management and cultural preservation, museumsaufsicht’s is gaining recognition as a skilled profession rather than a basic role.
This shift improves training standards and career pathways.
Greater Role in Community Engagement
Future museumsaufsicht’s roles may include more active engagement with visitors through interpretation support and inclusive practices. This evolution aligns supervision with education.
The role continues to grow beyond traditional boundaries.
Conclusion
I conclude by emphasizing that museumsaufsicht’s is far more than a background function. It is the backbone of museum operations, quietly ensuring that culture, history, and knowledge remain accessible and protected. By combining vigilance with empathy, structure with flexibility, and authority with service, museumsaufsicht’s embodies the values that museums stand for. Understanding this role deepens appreciation for museums not just as buildings or collections, but as carefully maintained spaces of shared human heritage.
Click Here For More Blog Posts!
FAQs
What does museumsaufsicht mean
Museumsaufsicht refers to museum supervision responsible for protecting exhibits, guiding visitors, and maintaining order.
Is museumsaufsicht the same as museum security
No, museumsaufsicht focuses on visitor interaction, cultural preservation, and ethical supervision rather than pure security enforcement.
Why is museumsaufsicht important
It protects irreplaceable collections and ensures a safe, respectful visitor environment.
What skills are needed for museumsaufsicht
Observation, communication, ethical judgment, and cultural awareness are essential skills.
Does museumsaufsicht affect visitor experience
Yes, professional museumsaufsicht enhances comfort, safety, and learning within the museum.